White bass Morone chrysops also known as silver bass or sand bass is a freshwater fish species found in North America. Hence, these fish are some of the most important fish in different aquatic ecosystems since they affect other fish and their environment in general.
Knowledge of white bass in aquatic environment resources includes but is not limited to their life history, habitat use and utilization, feeding behaviour, and the general influence of the species on other systems.
Physical Characteristics of White Bass
This fish must be identified by its silvery-white coloured fish with black mostly vertical stripes on the side of the body and a relatively deep, compressed body. Overall they have an average size of 10 to 14 inches and may weigh 1 to 2 pounds but some of them can attain a very large size.
Their slim-shaped bodies and split tails enable them to catch their prey in all water-bearing conditions, slow currents, or fast ones. White bass or more appropriately silver bass are inhabitants of the Mississippi River and can be switched in different freshwater bodies such as lakes, rivers, and reservoirs in the central east region of the United States.
Life Cycle of White Bass
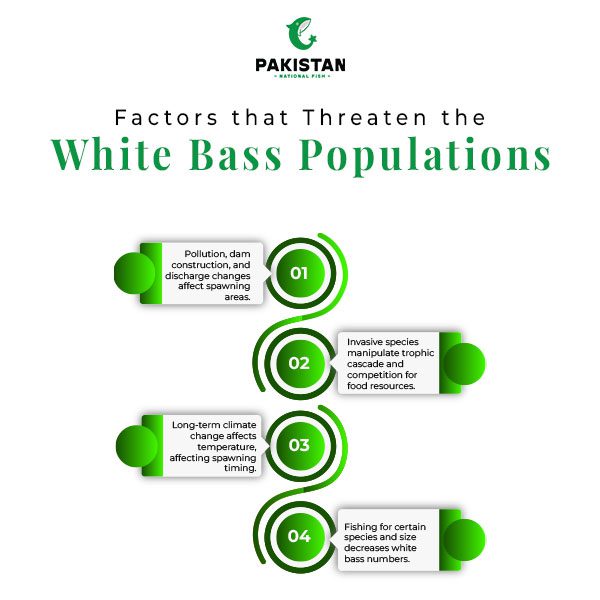
White bass also change their life cycle depending on the change in seasons with particular emphasis on their breeding activities which are affected by temperature. Spawning usually occurs in spring between water temperatures of 55-65°F (13-18°C). White bass are broadcast spawners, it is the males and females will release the eggs in the water and sperm where fertilization occurs. They are adhesive and the eggs attach themselves to rocks, plants; and other structures at the base of the water body and hatch after a few days.
White bass becomes sexually other at a length of about 7-9cm and an age of 2-3 years and have a life expectancy of 6 years or more in the wild. The reproductive success remains dependent on several physical characteristics of the water including water quality, temperature and freshness of the water, and the availability of food in the water which differ depending on water type either from lake, river, or sea.
Habitat Preferences of White Bass
These types of fish are real carnivores throughout their life cycle feeding on various prey according to available chances. Due to the feeding activity to prepare for spawning, fresh white bass becomes more accessible around the freshwater coastal and shoal zones in spring and early summer. In summer they go to deeper and cold water regions or grounds hence the name warm water fish. But they dive back into shallow waters during the early morning and early evenings to feed as their prey is normally abundant in the upper parts of the ocean.
Schooling is very common with white bass, and this is most apparent when feeding. These schools can encompass vast regions, and very often, pursuing baitfish will congregate them into a group that is rather easy to puzzle out. It also proves resourceful to the white sea bass but at the same time, it instigates chances for other higher-order predators, such as fish or birds to benefit from the concentrated prey.
Feeding Ecology of White Bass
Feeding patterns of the fish species are directly proportional to seasonal changes and water temperatures. White bass fishing is best during the spring and the fall when these fish are on a feeding spree due to the availability of small fish and invertebrates in waters with shallow depths. In winter their metabolism decreases, this is because water temperature decreases and thus their feeding rate is also decreased.
Like mahseer fish, white bass is environmentally balanced and acts to control the number of other fish species that inhabit the ecosystem. They feed on the smaller fish hence they are of great importance in someway regulating the populations of the forage fish so that they do not over multiply due to high demand as they are the small fish. This is important for the general health of the freshwater ecosystems since high levels of predation of, for example, plankton and algae by forage fish would be detrimental, leading to cases like algal blooms.
Important Ecological Role in Freshwater Habitat
White bass act as food for other large fishes including the largemouth bass, northern pike, walleye, and ospreys and herons. This places white bass a critical role in converting energy from low trophic levels which are made up of plankton and small fishes to upper trophic levels consisting of predator fishes and birds.
White bass as one of the fish species also contribute to nutrient cycling in their environment. They feed on their prey from all the different layers of the water and by their excretions the nutrients circulate within the water body. Therefore nutrient cycling is important in the productivity of both the aquatic food web and the environment such as periphyton growth and water quality.


